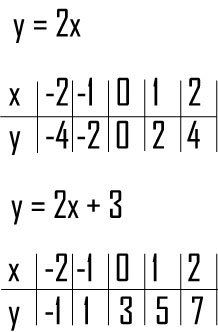y = mx + b
m is slope and b is y-intercept.
ex) Write the slope y-intercept form for the points (-2, 1) and (4, 4).
First find slope
= (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
= (4 - 1)/(4 - (-2))
= 3/6
= 0.5 or 1/2
Now that we have a y-coordinate, the slope and an x-coordinate we can find the y-intercept.
b = y - mx
b = 4 - .5(4)
b = 4 - 2
b = 2
y = 0.5x + 2
http://www.gomath.com/exercises/SlopeEquationYintercept.php
http://www.learningwave.com/lwonline/algebra_section2/yintercept2.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_equation
Thursday, March 22, 2007
Midpoint
Distance
Distance - In the mathematical subfield of graph theory we can define a notion of distance between two vertices in a graph. The extent or account of space between two objects or points.
Find the distance between
A(-2, 3) and B(8, -1).
d = SQRT[(8 - (-2))^2 + (-1 - 3)^2]
Simplify.
d = SQRT[(10)^2 + (-4)^2]
d = SQRT(100 + 16)
d = SQRT(116)
d = 10.77units
http://library.thinkquest.org/20991/geo/coordgeo.html#distance
Find the distance between
A(-2, 3) and B(8, -1).
d = SQRT[(8 - (-2))^2 + (-1 - 3)^2]
Simplify.
d = SQRT[(10)^2 + (-4)^2]
d = SQRT(100 + 16)
d = SQRT(116)
d = 10.77units
http://library.thinkquest.org/20991/geo/coordgeo.html#distance
Wednesday, March 21, 2007
Slope
Slope - In mathematics, the slope of a straight line (within a Cartesian coordinate system) is a measure for the "steepness" of said line. With an understanding of algebra and geometry, one can calculate the slope of a straight line; with calculus, one can calculate the slope of the tangent to a curve at a point.


Tuesday, March 20, 2007
Zooms
1) ZBox -allows you to draw a box to define the viewing window.
2) Zoom In -magnifies the graph around the cursor.
3) Zoom Out-displays more of the graph around the cursor
4) ZDecimal- sets the change in X and Y to Increments of 0.1 when you use trace
5) ZSquare- Adjusts the viewing window so that X and Y dimensions are equal
6) ZStandard- Sets the standard (default) window variables
7) ZTrig- Sets the built in Trigonometry window variables
8) ZInteger- After you position the cursor and press Enter, sets the change in X and Y to whole number increments
9) Zoom Stat- Sets the variables for currently defined statistical lists
0)Zoom Fit-Fits Y-min and Y-max between X-min and X-max
2) Zoom In -magnifies the graph around the cursor.
3) Zoom Out-displays more of the graph around the cursor
4) ZDecimal- sets the change in X and Y to Increments of 0.1 when you use trace
5) ZSquare- Adjusts the viewing window so that X and Y dimensions are equal
6) ZStandard- Sets the standard (default) window variables
7) ZTrig- Sets the built in Trigonometry window variables
8) ZInteger- After you position the cursor and press Enter, sets the change in X and Y to whole number increments
9) Zoom Stat- Sets the variables for currently defined statistical lists
0)Zoom Fit-Fits Y-min and Y-max between X-min and X-max
Domain and Range
Domain -all real numbers (x1,x2=infinity)
Range -all real numbers (y1,y2=infinity)
Example: find the range of the relation in the arrow diagram?
3 -- 9
-6 -- 2
5 -- 10
R= {9,2,10}
and the Domain would be D={3,-6, 5}
This is a graph of y=2-x
the x-intercept is at (2,0) and the y-intercept is at (0,-2)

Range -all real numbers (y1,y2=infinity)
Example: find the range of the relation in the arrow diagram?
3 -- 9
-6 -- 2
5 -- 10
R= {9,2,10}
and the Domain would be D={3,-6, 5}
This is a graph of y=2-x
the x-intercept is at (2,0) and the y-intercept is at (0,-2)

d={" all real numbers"}
r={"all real numbers"}
Monday, March 19, 2007
MODE
Numeric Notation
- Normal
- Sci (scientific)
- Eng (engineering)
Decimal
- Float: lets the number of the decimal place change based on the result (up to 10 digits)
- 0-9: Sets the number of decimal places to a value that you specify
Angle of Measure
- Radian: intercepts angle values as radians
- Degrees: Intercepts angle values as degrees
Type of Graph
- Func (functional): plots functions, where Y is a function of X
- Par (parametric): plots functions were X and Y are functions of T
- Pol (polar): plots functions where r is a function of [n] "theta"
- Seq (sequence): plots sequences
Sequential: draws graphs one at a time
Simul (simultaneous): draws several graphs at one time
Real or Complex mode
- Real: displays real numbers
- a+bi (rectangular complex): displays as 3+2i
- re^"theta"i (polar complex): displays as re^"theta"i
Screen Display
- Full: displays full screen
- Horiz: displays a horizontal split screen
- G-T: displays vertical split screen
- Normal
- Sci (scientific)
- Eng (engineering)
Decimal
- Float: lets the number of the decimal place change based on the result (up to 10 digits)
- 0-9: Sets the number of decimal places to a value that you specify
Angle of Measure
- Radian: intercepts angle values as radians
- Degrees: Intercepts angle values as degrees
Type of Graph
- Func (functional): plots functions, where Y is a function of X
- Par (parametric): plots functions were X and Y are functions of T
- Pol (polar): plots functions where r is a function of [n] "theta"
- Seq (sequence): plots sequences
Sequential: draws graphs one at a time
Simul (simultaneous): draws several graphs at one time
Real or Complex mode
- Real: displays real numbers
- a+bi (rectangular complex): displays as 3+2i
- re^"theta"i (polar complex): displays as re^"theta"i
Screen Display
- Full: displays full screen
- Horiz: displays a horizontal split screen
- G-T: displays vertical split screen
Plot/Linear Regression
Plot
Method: Collect/Gather data. Determine which data might be dependent on the other.
ex) hours studied vs. test scores. Test score depends on hours studied.
Dependent Variable (y-axis, L2), Independent Variable (x-axis, L1)

You plot these points on your calculator by pushing STAT, Edit... Under L1 you put the hours studied and under the L2 you put the test score. To see your graph you push GRAPH.
If your graph doesn't appear push Y= and turn on Plot1.
Line of Best Fit (Linear Regression)
After plotting your points you can "see" the line of best fit by pushing:
STAT, CALC, 4:LinReg (ax+b), ENTER, 2nd, 1(L1), "comma", 2nd, 2(L2), "comma", VARS, Y-VARS, 1:Function, 1:Y1, ENTER, ENTER, GRAPH
To see the equation go to Y=
Method: Collect/Gather data. Determine which data might be dependent on the other.
ex) hours studied vs. test scores. Test score depends on hours studied.
Dependent Variable (y-axis, L2), Independent Variable (x-axis, L1)

You plot these points on your calculator by pushing STAT, Edit... Under L1 you put the hours studied and under the L2 you put the test score. To see your graph you push GRAPH.
If your graph doesn't appear push Y= and turn on Plot1.
Line of Best Fit (Linear Regression)
After plotting your points you can "see" the line of best fit by pushing:
STAT, CALC, 4:LinReg (ax+b), ENTER, 2nd, 1(L1), "comma", 2nd, 2(L2), "comma", VARS, Y-VARS, 1:Function, 1:Y1, ENTER, ENTER, GRAPH
To see the equation go to Y=
Simplifying Radicals (perfect squares)
1. Find the largest perfect square
SQRT (48) = 16
2. Write as the product of the perfect squares
SQRT (16 * 3) then SQRT(16)SQRT(3)
3. Reduce the "perfect" radical
SQRT(16)SQRT(3) = 4SQRT(3)
REDUCE: 3SQRT(50)
3SQRT(25 * 2) then 3SQRT(25)SQRT(2)
3*5SQRT(2) = 15SQRT(2)
SQRT (48) = 16
2. Write as the product of the perfect squares
SQRT (16 * 3) then SQRT(16)SQRT(3)
3. Reduce the "perfect" radical
SQRT(16)SQRT(3) = 4SQRT(3)
REDUCE: 3SQRT(50)
3SQRT(25 * 2) then 3SQRT(25)SQRT(2)
3*5SQRT(2) = 15SQRT(2)
Friday, March 16, 2007
Inequalities (Graphing in 1-D)
-Flip the inequality sign only when multiplying or dividing by negatives.
-open circle = greater/less than
-closed circel = equal to and greater/less than
-solve inequality as if solving a "regular" equation (with an equal sign)
ex) http://webgraphing.com/examples_inequality_1d.jsp
-open circle = greater/less than
-closed circel = equal to and greater/less than
-solve inequality as if solving a "regular" equation (with an equal sign)
ex) http://webgraphing.com/examples_inequality_1d.jsp
Number Sets
Natural N = {1, 2, 3...}
Whole W = {0, 1, 2, 3...}
Integer I = {... -2, -1, 0, 1, 2...}
Rational Q = {a/b; a, b "in the set" I, b "is not equal to" 0}
Decimal must terminate
Irrational IQ = Not in the set of Q
Real R = Q "and" IQ


The second diagram wasn't included in the lesson but, It has examples of N, W, I, Q, IQ, and R numbers.
Whole W = {0, 1, 2, 3...}
Integer I = {... -2, -1, 0, 1, 2...}
Rational Q = {a/b; a, b "in the set" I, b "is not equal to" 0}
Decimal must terminate
Irrational IQ = Not in the set of Q
Real R = Q "and" IQ


The second diagram wasn't included in the lesson but, It has examples of N, W, I, Q, IQ, and R numbers.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)